Vulnerability Management: Secure Your Systems Before Hackers Do

Vulnerability management is a critical cybersecurity process that involves identifying, classifying, remediating, and mitigating software and hardware vulnerabilities to reduce an organization’s exposure to cyber threats and prevent potential data breaches.
In today’s digital landscape, organizations face a constant barrage of cyber threats. One of the most effective ways to protect your systems and data is through robust vulnerability management: How to Identify and Patch Security Flaws Before Hackers Exploit Them.
Understanding Vulnerability Management
Vulnerability management is more than just running a scan; it’s a proactive, continuous process that helps organizations identify, assess, and remediate weaknesses in their IT infrastructure. This process is essential to minimizing the risk of exploitation by cybercriminals.
What is a Vulnerability?
A vulnerability is a weakness or flaw in software, hardware, or a system that a threat actor could exploit to gain unauthorized access, disrupt operations, or steal data. These vulnerabilities can arise from coding errors, design flaws, or misconfigurations.
Why is Vulnerability Management Important?
Effective vulnerability management is crucial for:
- Reducing the attack surface and minimizing the risk of breaches.
- Complying with industry regulations and standards.
- Maintaining business continuity and avoiding costly downtime.
- Protecting sensitive data and maintaining customer trust.
Without a structured approach to identifying and fixing vulnerabilities, organizations are sitting ducks for cyberattacks. Regular vulnerability assessments and timely patching are the cornerstones of any robust cybersecurity posture.
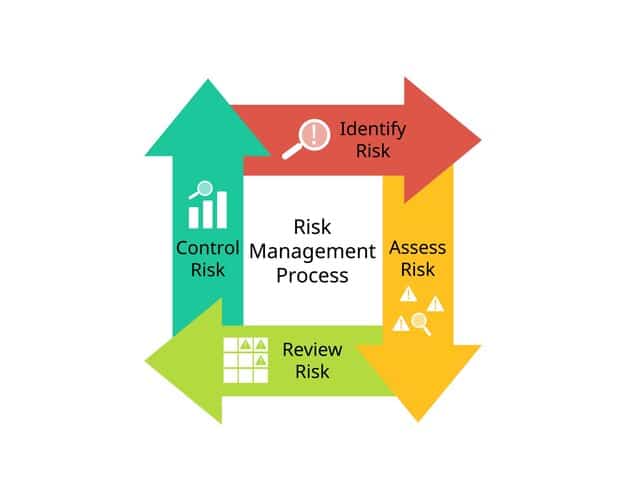
The Vulnerability Management Lifecycle
The vulnerability management lifecycle provides a structured approach to managing vulnerabilities, ensuring that they are identified, assessed, and remediated in a timely and efficient manner. This cyclical process helps organizations stay ahead of emerging threats.
Step 1: Identification
This involves discovering and cataloging vulnerabilities in your IT environment. Common methods include:
- Vulnerability scanners: Automated tools that scan systems and applications for known vulnerabilities.
- Penetration testing: Simulated attacks to identify weaknesses and assess the effectiveness of security controls.
- Security audits: Comprehensive reviews of security policies, procedures, and configurations.
Step 2: Assessment
Once vulnerabilities are identified, they need to be assessed to determine their potential impact and likelihood of exploitation. This involves:
- Prioritizing vulnerabilities based on severity, exploitability, and potential impact.
- Determining the affected systems and applications.
- Analyzing the potential business impact of a successful exploit.
Step 3: Remediation
This is the process of fixing or mitigating vulnerabilities. Common remediation strategies include:
- Patching: Applying software updates to fix known vulnerabilities.
- Configuration changes: Modifying system settings to eliminate weaknesses.
- Workarounds: Implementing temporary solutions to reduce the risk of exploitation.
Step 4: Verification
After remediation, it’s essential to verify that the vulnerabilities have been successfully fixed. This can be done through rescanning, penetration testing, or manual testing.
By following the vulnerability management lifecycle, organizations can continuously improve their security posture and reduce their exposure to cyber threats. Consistent execution of each step is paramount.
Vulnerability Scanning: Tools and Techniques
Vulnerability scanning is a fundamental component of vulnerability management. It involves using automated tools to identify known vulnerabilities in systems, networks, and applications. Selecting the right tools and techniques is critical for effective scanning.
Types of Vulnerability Scanners
There are several types of vulnerability scanners, each with its strengths and weaknesses:
- Network scanners: Identify vulnerabilities in network devices, servers, and other infrastructure components.
- Web application scanners: Focus on identifying vulnerabilities in web applications, such as cross-site scripting (XSS) and SQL injection.
- Host-based scanners: Installed on individual systems to identify vulnerabilities in the operating system and installed software.
Choosing the Right Scanner
When selecting a vulnerability scanner, consider the following factors:
- Coverage: Does the scanner support the technologies and platforms used in your environment?
- Accuracy: How accurate are the scanner’s results? Does it produce a lot of false positives?
- Scalability: Can the scanner handle the size and complexity of your IT environment?
Best Practices for Vulnerability Scanning
To get the most out of vulnerability scanning, follow these best practices:
- Scan regularly: Schedule scans on a regular basis, such as weekly or monthly.
- Authenticate scans: Authenticated scans provide more accurate results by accessing system configuration information.
- Prioritize results: Focus on remediating the most critical vulnerabilities first.
Effective vulnerability scanning provides organizations with valuable insights into their security posture, enabling them to proactively address weaknesses before they can be exploited. It’s a key component of a proactive cybersecurity strategy.

Prioritizing and Remediating Vulnerabilities
Identifying vulnerabilities is only half the battle. Organizations must also prioritize and remediate vulnerabilities effectively to minimize their risk. This involves assessing the impact and likelihood of exploitation, and then taking appropriate action.
Risk-Based Prioritization
Prioritize vulnerabilities based on the following factors:
- Severity: How critical is the vulnerability? Can it lead to remote code execution or data theft?
- Exploitability: Is there a known exploit for the vulnerability? How easy is it to exploit?
- Business impact: What is the potential impact on the business if the vulnerability is exploited?
Remediation Strategies
Common remediation strategies include:
- Patching: Apply software updates to fix known vulnerabilities. This is the most common and effective remediation method.
- Configuration changes: Modify system settings to eliminate weaknesses. For example, disabling unnecessary services or hardening security configurations.
- Workarounds: Implement temporary solutions to reduce the risk of exploitation. This may involve disabling a feature or implementing a compensating control.
Patch Management Best Practices
Effective patch management is crucial for timely remediation. Follow these best practices:
- Establish a patch management policy: Define clear roles and responsibilities for patch management.
- Test patches before deployment: Test patches in a non-production environment before deploying them to production systems.
- Automate patch deployment: Use patch management tools to automate the patch deployment process.
By prioritizing and remediating vulnerabilities based on risk, organizations can focus their resources on the most critical threats and reduce their overall risk exposure. This approach ensures that limited resources are used effectively.
Integrating Vulnerability Management into Security Operations
Vulnerability management should not be a siloed activity; it should be integrated into an organization’s overall security operations. This integration allows for better coordination, communication, and response to vulnerabilities.
Integrating with SIEM
Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems can be integrated with vulnerability scanners to provide real-time visibility into vulnerabilities.
Integrating with Threat Intelligence
Threat intelligence feeds can provide valuable information about emerging threats and vulnerabilities. Integrating threat intelligence with vulnerability management can help organizations prioritize and remediate the most relevant threats.
Establishing a Vulnerability Response Plan
A vulnerability response plan outlines the steps to take when a vulnerability is discovered. It should include:
- Roles and responsibilities.
- Communication procedures.
- Escalation paths.
Proper integration of vulnerability management into security operations ensures that the organization has a holistic view of its security posture and can respond effectively to emerging threats. Constant vigilance and proactive measures are key.
The Future of Vulnerability Management
The landscape of vulnerability management is constantly evolving. Emerging technologies and trends are shaping the future of this critical security practice.
Automation and AI
Automation and artificial intelligence (AI) are playing an increasingly important role in vulnerability management. AI-powered tools can automate vulnerability scanning, prioritize vulnerabilities, and even recommend remediation strategies.
Cloud Vulnerability Management
As more organizations move to the cloud, cloud vulnerability management is becoming increasingly important. Cloud vulnerability management tools can scan cloud environments for misconfigurations and vulnerabilities, ensuring that cloud resources are properly secured.
DevSecOps
DevSecOps integrates security into the software development lifecycle. This involves incorporating security testing and vulnerability scanning into the development process, ensuring that vulnerabilities are identified and addressed early on.
The future of vulnerability management is focused on automation, integration, and proactive security. By embracing these trends, organizations can stay ahead of emerging threats and maintain a strong security posture. Continuous learning and adaptation are crucial in this ever-changing landscape.
| Key Point | Brief Description |
|---|---|
| 🛡️ Identification | Discover vulnerabilities using scanners, tests, and audits. |
| ⚠️ Assessment | Prioritize vulnerabilities based on severity and impact. |
| 🛠️ Remediation | Apply patches, change configurations, or use workarounds. |
| ✔️ Verification | Verify that the vulnerability has been successfully fixed. |
Frequently Asked Questions
▼
Vulnerability management aims to reduce an organization’s exposure to cyber threats by identifying and mitigating security flaws before they can be exploited by attackers.
▼
Vulnerability scans should be performed regularly, ideally weekly or monthly, but more frequently for critical systems or after significant changes to the IT environment.
▼
Vulnerability scanning is automated to identify known vulnerabilities, while penetration testing is a simulated attack to exploit weaknesses and assess the effectiveness of security controls.
▼
Common strategies include patching software, modifying configurations, or implementing temporary workarounds to reduce the risk associated with a known vulnerability.
▼
By providing organizations with insights into emerging threats and vulnerabilities, threat intelligence helps prioritize and remediate the most relevant and critical risks promptly.
Conclusion
Effective vulnerability management is an ongoing process that requires a proactive approach. By implementing a robust vulnerability management program, organizations can significantly reduce their risk of cyberattacks and protect their valuable data.





