Zero Trust Fintech: Secure Your Infrastructure in 2025

Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA) in fintech requires verifying every digital interaction within the ecosystem, mitigating insider threats and data breaches. This step-by-step guide outlines key strategies for implementing ZTA to protect fintech infrastructure by 2025, ensuring enhanced security and compliance.
In the rapidly evolving landscape of financial technology (fintech), cybersecurity has become paramount. Implementing a
Architecture: A Step-by-Step Guide to Securing Your Fintech Infrastructure in 2025
is not just a recommendation; it’s a necessity to protect against increasingly sophisticated cyber threats.
Understanding the Zero Trust Architecture for Fintech
The
is a security framework that operates on the principle of “never trust, always verify.” This approach is crucial for fintech companies, where data breaches and cyberattacks can lead to significant financial and reputational damage. Applying ZTA to fintech infrastructure involves several key steps.
What is Zero Trust?
Zero Trust is a security model that assumes no user or device, whether inside or outside the network, should be automatically trusted. Instead, every access request is fully authenticated, authorized, and encrypted before granting access. This approach significantly reduces the attack surface and minimizes the impact of potential breaches.
Why is Zero Trust Important for Fintech?
Fintech companies handle sensitive financial data, making them attractive targets for cybercriminals. Traditional security models, which rely on perimeter-based defenses, are often inadequate in protecting against modern threats.
offers a more robust security posture by continuously verifying every user and device, preventing unauthorized access and limiting the spread of attacks.
- Data Protection: Ensures sensitive data is protected through encryption and access controls.
- Compliance: Helps meet regulatory requirements such as GDPR and PCI DSS.
- Risk Mitigation: Reduces the risk of data breaches and financial losses.
- Enhanced Security: Provides a more comprehensive and adaptable security framework.
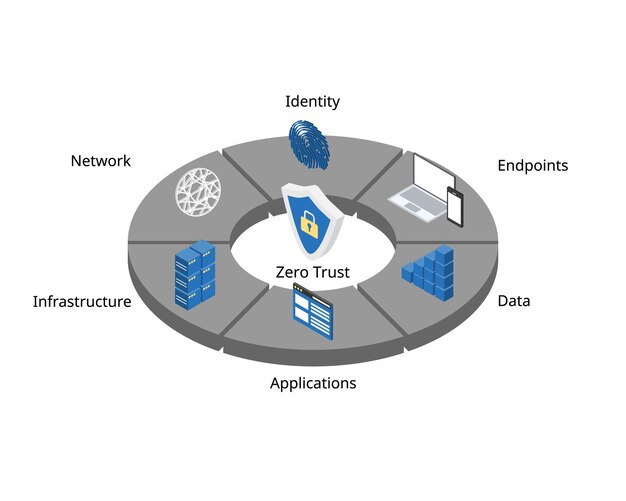
By understanding the core principles of
, fintech companies can build a resilient security infrastructure that safeguards their assets and customer data. This proactive approach is essential for maintaining trust and ensuring long-term success in the competitive fintech landscape.
Step 1: Assess Your Current Fintech Security Infrastructure
Before implementing
, it’s crucial to evaluate your existing security measures. This assessment provides a baseline for identifying vulnerabilities and areas that need improvement. A thorough understanding of your current security posture is the first step towards building a robust ZTA framework.
Identify Critical Assets
Start by identifying your most valuable assets, such as customer data, financial records, and intellectual property. Understanding where these assets are stored and how they are accessed is essential for prioritizing security efforts. Focus on protecting the assets that would cause the most damage if compromised.
Evaluate Existing Security Controls
Examine your current security controls, including firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and access management policies. Determine whether these controls are effective in preventing unauthorized access and detecting potential threats. Look for gaps in your security architecture that could be exploited by attackers.
Key areas to evaluate include:
- Network Security: Assess the effectiveness of your firewalls and network segmentation.
- Endpoint Security: Evaluate the security of devices accessing your network.
- Identity and Access Management: Review your user authentication and authorization processes.
- Data Encryption: Ensure sensitive data is encrypted both in transit and at rest.
A comprehensive assessment of your current security infrastructure provides valuable insights into the areas that require the most attention. This knowledge is crucial for developing a well-informed and effective implementation strategy.
Step 2: Implement Strong Identity and Access Management (IAM)
Strong Identity and Access Management (IAM) is the foundation of
. It ensures that only authorized users and devices can access sensitive resources. Implementing robust IAM practices is essential for preventing unauthorized access and mitigating insider threats.
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
MFA adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide multiple forms of identification before granting access. This could include something they know (password), something they have (security token), or something they are (biometrics). MFA significantly reduces the risk of account compromise.
Least Privilege Access
The principle of least privilege dictates that users should only have access to the resources they need to perform their job functions. This limits the potential damage that can be caused by a compromised account. Regularly review and adjust access permissions to ensure they align with users’ current roles and responsibilities.

Effective IAM practices include:
- Centralized User Management: Use a centralized IAM system to manage user identities and access permissions.
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Assign access permissions based on user roles rather than individual users.
- Regular Audits: Conduct regular audits of user access permissions to identify and correct any discrepancies.
By implementing strong IAM practices, fintech companies can significantly enhance their security posture and reduce the risk of unauthorized access to sensitive data. This is a critical component of a comprehensive
framework.
Step 3: Network Segmentation and Microsegmentation
Network segmentation and microsegmentation are essential techniques for limiting the impact of potential breaches. By dividing the network into smaller, isolated segments, organizations can prevent attackers from moving laterally and accessing critical resources.
What is Network Segmentation?
Network segmentation involves dividing the network into logical or physical segments, each with its own security policies and access controls. This prevents attackers from gaining access to the entire network if they compromise a single segment. Segmentation can be based on factors such as department, application, or data sensitivity.
What is Microsegmentation?
Microsegmentation takes network segmentation a step further by creating even smaller, more granular segments. This allows for more precise control over access to individual workloads and applications. Microsegmentation is particularly useful in cloud environments, where workloads are often distributed across multiple servers and virtual machines.
Key benefits of network segmentation and microsegmentation include:
- Reduced Attack Surface: Limits the scope of potential breaches by isolating critical resources.
- Improved Threat Containment: Prevents attackers from moving laterally within the network.
- Enhanced Compliance: Helps meet regulatory requirements by isolating sensitive data.
Implementing network segmentation and microsegmentation requires careful planning and execution. It’s essential to identify the critical resources that need to be protected and to define clear security policies for each segment. Regular monitoring and testing are also crucial for ensuring the effectiveness of these controls.
Step 4: Continuous Monitoring and Threat Detection
Continuous monitoring and threat detection are essential for identifying and responding to cyber threats in real-time. By continuously monitoring network activity and system logs, organizations can detect suspicious behavior and take immediate action to prevent potential breaches. This proactive approach is crucial for maintaining a strong security posture.
Security Information and Event Management (SIEM)
SIEM systems collect and analyze security data from various sources, including network devices, servers, and applications. This data is used to identify potential threats and generate alerts. SIEM systems can also provide valuable insights into security trends and patterns, helping organizations to improve their overall security posture.
User and Entity Behavior Analytics (UEBA)
UEBA systems use machine learning to detect anomalous behavior by users and devices. This can include unusual login patterns, unauthorized access attempts, and suspicious data transfers. UEBA systems can help identify insider threats and compromised accounts, enabling organizations to take immediate action to prevent potential breaches.
Effective continuous monitoring and threat detection practices include:
- Real-Time Monitoring: Continuously monitor network activity and system logs for suspicious behavior.
- Automated Threat Detection: Use automated tools to identify and respond to potential threats.
- Incident Response Plan: Develop a comprehensive incident response plan to guide the response to security incidents.
By implementing continuous monitoring and threat detection, fintech companies can significantly improve their ability to detect and respond to cyber threats. This is a critical component of a comprehensive
framework.
Step 5: Data Encryption and Protection
Data encryption and protection are essential for safeguarding sensitive financial information. By encrypting data both in transit and at rest, organizations can prevent unauthorized access and protect against data breaches. A robust data protection strategy is crucial for maintaining customer trust and complying with regulatory requirements.
Encryption in Transit
Encryption in transit ensures that data is protected while it is being transmitted between systems. This is typically achieved using protocols such as Transport Layer Security (TLS) and Secure Sockets Layer (SSL). Encryption in transit prevents attackers from intercepting and reading sensitive data as it is being transmitted.
Encryption at Rest
Encryption at rest protects data while it is stored on disks, databases, and other storage devices. This is typically achieved using encryption algorithms such as Advanced Encryption Standard (AES). Encryption at rest prevents unauthorized access to data even if storage devices are lost or stolen.
Effective data encryption and protection practices include:
- End-to-End Encryption: Encrypt data from the point of origin to the point of destination.
- Key Management: Implement a robust key management system to protect encryption keys.
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP): Use DLP tools to prevent sensitive data from leaving the organization.
By implementing data encryption and protection, fintech companies can significantly reduce the risk of data breaches and protect sensitive financial information. This is a critical component of a comprehensive
framework.
Step 6: Automate and Orchestrate Security Responses
Automating and orchestrating security responses is crucial for improving efficiency and reducing response times. By automating routine security tasks and orchestrating responses to complex threats, organizations can free up valuable resources and improve their overall security posture. This is particularly important in the fast-paced fintech environment, where rapid response times are essential for mitigating potential damage.
Security Automation
Security automation involves using automated tools to perform routine security tasks such as vulnerability scanning, patch management, and incident response. This can reduce the workload on security teams and improve the speed and accuracy of security operations. Automation can also help to enforce security policies and ensure consistency across the organization.
Security Orchestration
Security orchestration involves integrating various security tools and systems to create a coordinated response to security incidents. This can include automating the process of isolating infected systems, blocking malicious traffic, and notifying relevant stakeholders. Orchestration can significantly reduce response times and minimize the impact of potential breaches.
Effective automation and orchestration practices include:
- Playbooks: Develop detailed playbooks for responding to common security incidents.
- Integration: Integrate security tools and systems to create a coordinated response.
- Testing: Regularly test automated responses to ensure they are effective.
By implementing automation and orchestration, fintech companies can significantly improve their ability to respond to security incidents and protect their assets. This is a critical component of a proactive
framework.
| Key Aspect | Brief Description |
|---|---|
| 🛡️ IAM Implementation | Multi-Factor Authentication and Least Privilege Access. |
| 🔍 Network Segmentation | Dividing network to isolate segments and reduce threat movement. |
| 🚨 Threat Detection | Continuous real-time monitoring with SIEM/UEBA. |
| 🔒 Data Encryption | Protect data at rest and in transit. |
Frequently Asked Questions
▼
The primary goal is to enhance security by verifying every user and device, both inside and outside the network, before granting access to resources, thus mitigating the risk of unauthorized access and data breaches.
▼
MFA adds an additional layer of security by requiring users to provide multiple forms of identification, such as passwords and security tokens, making it significantly harder for attackers to compromise accounts.
▼
Network segmentation divides the network into isolated segments, limiting the scope of potential breaches by preventing attackers from moving laterally and accessing critical resources throughout the entire network.
▼
Continuous monitoring enables real-time detection of suspicious activities and potential threats, ensuring rapid incident response and preventing unauthorized access or data breaches before significant damage occurs.
▼
Data encryption ensures that sensitive information is protected both in transit and at rest, preventing unauthorized access even if storage devices are compromised, thus safeguarding customer data and maintaining regulatory compliance.
Conclusion
Implementing a
is essential for securing fintech infrastructure in 2025. By following these steps, fintech companies can build a robust security framework that protects against increasingly sophisticated cyber threats and ensures long-term success.